On May 31st, 2024, Snowflake issued a joint statement with CrowdStrike and Mandiant stating that they are investigating a targeted campaign against Snowflake users with single-factor authentication.
There is no evidence to suggest vulnerabilities in Snowflake's product or any data exfiltration caused by compromised credentials of a current or former Snowflake employee.
If you are a Snowflake customer, it's important to read the company's guidance on preventing unauthorized access and ensure your environment is properly configured and sufficiently monitored.
The Varonis Threat Labs team performed threat hunting queries and proactive posture checks for our Varonis for Snowflake customer tenants over the weekend and confirmed there is no evidence of compromise in accounts we're monitoring.
What does this mean for my organization?
Given the importance of data stored in Snowflake databases and warehouses, compromised credentials can lead to significant data breaches.
Once an attacker has control of an identity in cloud-hosted applications, there is no perimeter. It's essential to ensure that if an identity is compromised, there are additional lines of defense between the bad actor and your sensitive data.
It is crucial for customers to:
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Regularly rotate API and OAuth keys
- Monitor for unusual account activity
Snowflake has published a security bulletin with Indicators of Compromise (IoCs), investigative queries, and advice on securing accounts. According to the bulletin, customers should review their account activity, implement stricter security protocols, and follow recommended practices for API key management.
Snowflake has identified the IP addresses associated with suspicious activity, which we've included below.
Additionally, connections from clients identifying as 'rapeflake' or 'DBeaver_DBeaverUltimate' running on Windows Server 2022 should be scrutinized, as they are known to be associated with data exfiltration.
For more details and queries you can run, please refer to the Snowflake security bulletin.
Snowflake security health check with Varonis
The Varonis Threat Labs team also performs threat hunting and proactive posture checks when incidents like this happen. Our main goal is to ensure any customers using Varonis to monitor Snowflake are protected, even if their SOC teams aren't aware of the attack campaign.
The Varonis platform provides enhanced visibility and security for your critical Snowflake data and the underlying cloud infrastructure. We make the recommended steps offered by the Snowflake security team quick and easy while offering additional data security posture checks and threat detection capabilities to ensure your Snowflake data is resilient to attack vectors beyond what is currently being observed.
Step 1: Enforce multifactor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO)
Varonis will identify Snowflake users who do not have MFA enabled, including users with elevated permissions. This is priority #1, given the credential stuffing tactic observed in the wild. If your Varonis install is connected to Okta, we can also isolate users who have direct access to Snowflake instead of authenticating via SSO.
Step 1: Quickly isolate Snowflake users without MFA enabled.
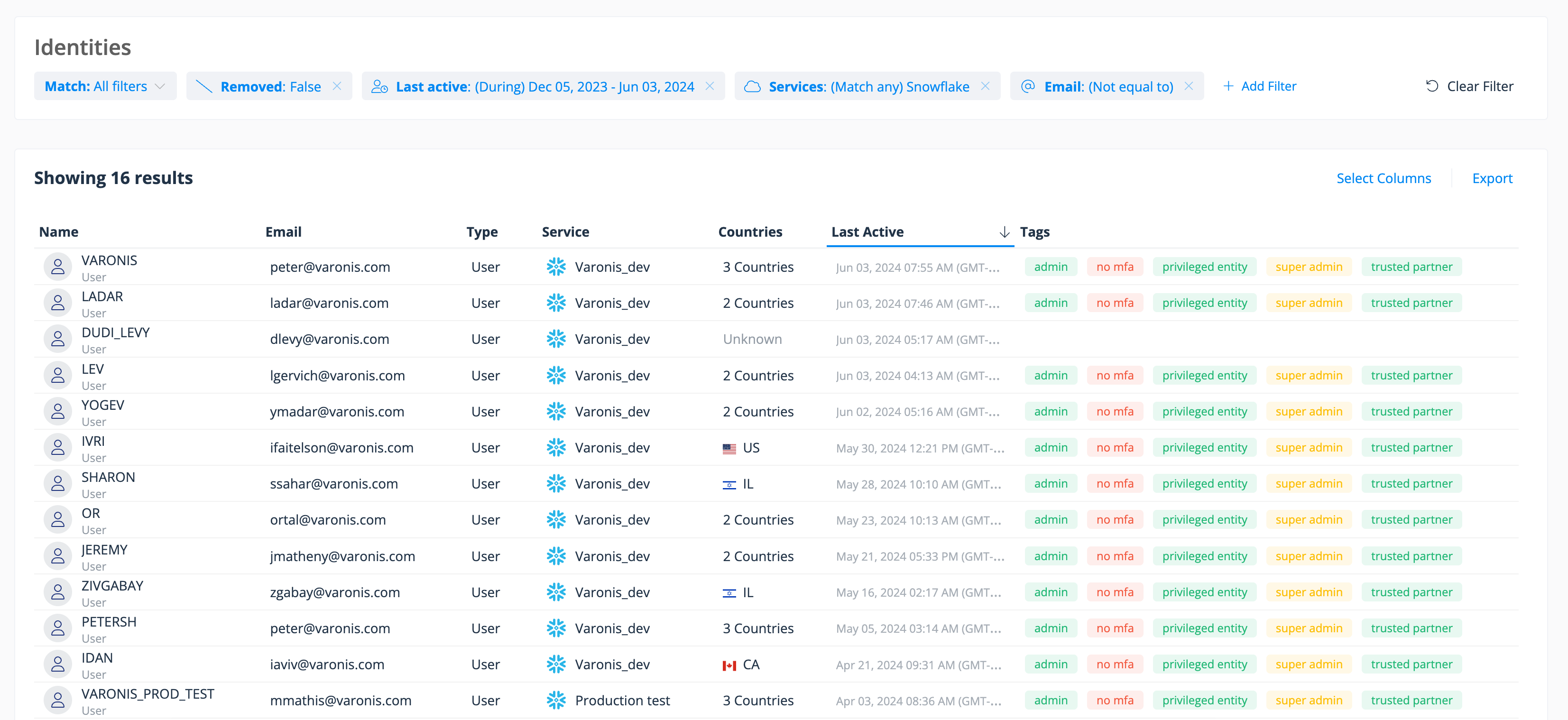
Step 1: Quickly isolate Snowflake users without MFA enabled.
Step 2: Identify sensitive data exposure
Varonis helps you understand what actions users and groups can perform on your critical data and where it is potentially overexposed internally, externally, or publicly. For Snowflake, customers often use Varonis to alert them to data that has been published on the Snowflake marketplace or exported to public stages in AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
You can also use this analysis to hunt for and eliminate excessive and/or stale permissions to reduce your blast radius and minimize the damage inflicted by compromised users or insider threats.
Step 2: Check for overexposed data in Snowflake due to risky misconfigurations or excessive permissions.
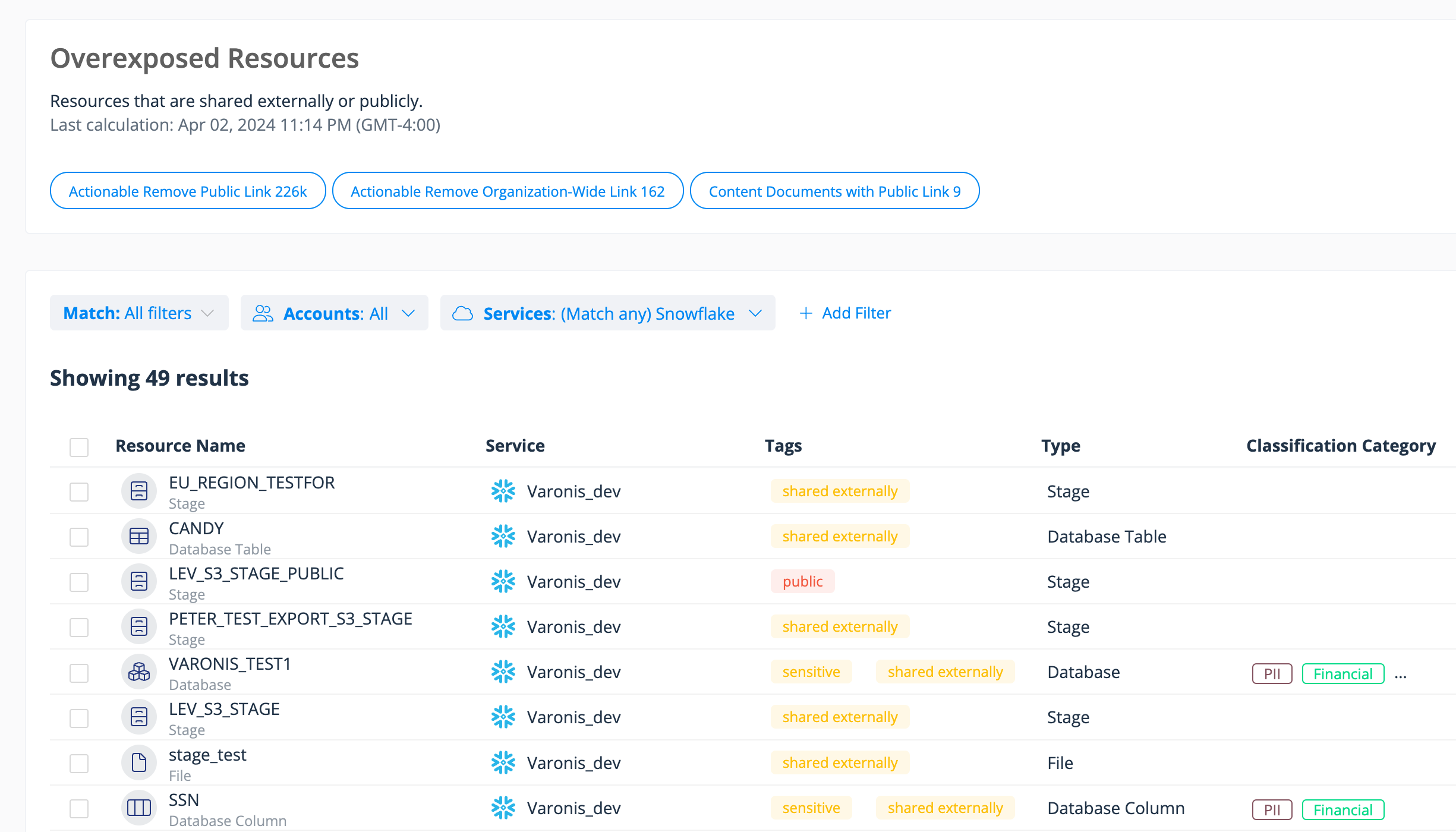
Step 2: Check for overexposed data in Snowflake due to risky misconfigurations or excessive permissions.
Step 3: Audit sensitive data access activity
Use Varonis' audit trail to search for risky actions such as users dropping tables or performing queries to exfiltrate data. You can filter activity based on the suspicious IP addresses provided by the Snowflake team or by facets such as country, user, device name, and other IOCs. If you do find signs of compromise, you can pivot across other data stores.
Step 3: Query your logs for sensitive data access and other risky actions. Filter by IP address, user, device name, etc.
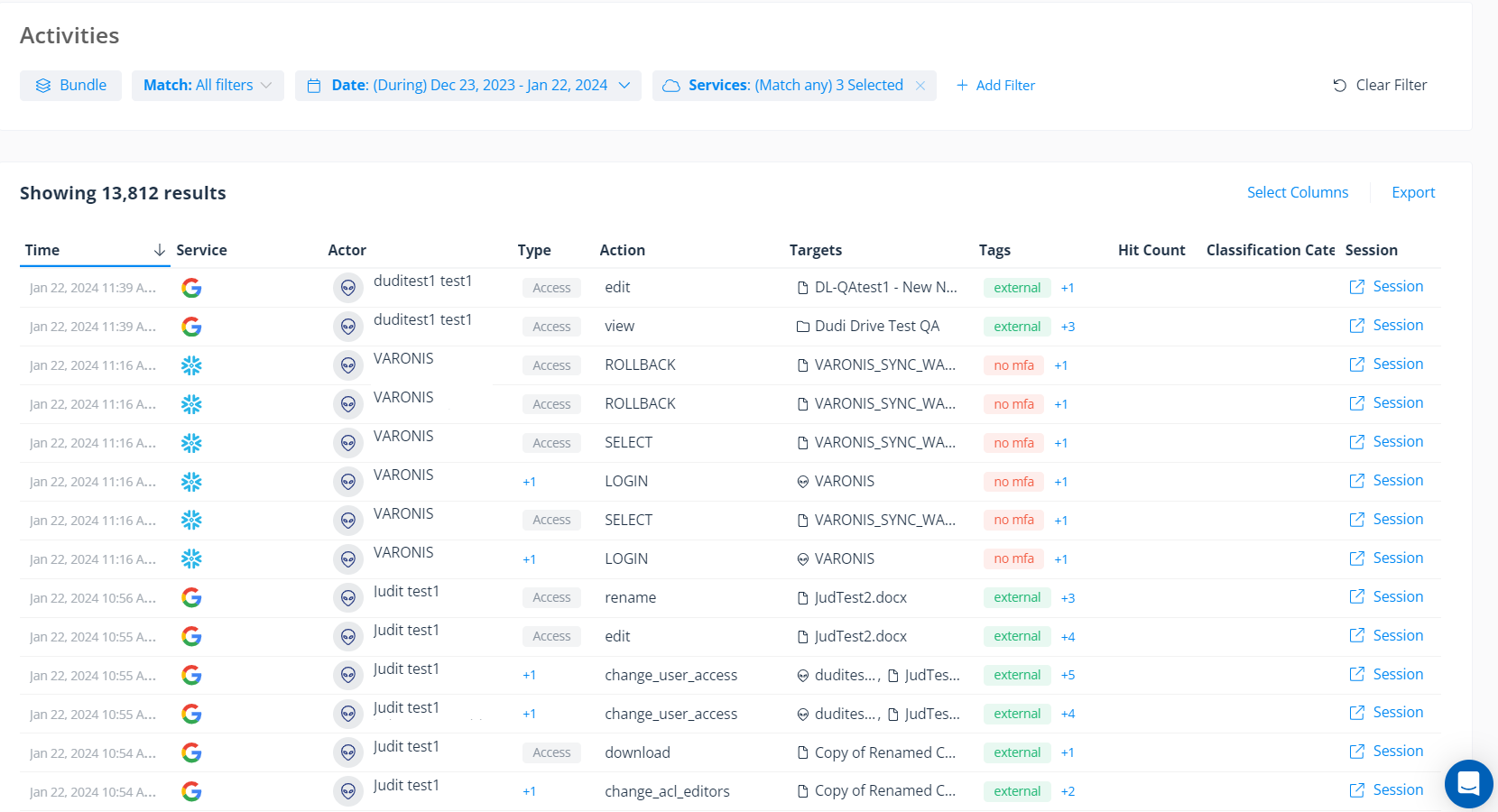
Step 3: Query your logs for sensitive data access and other risky actions. Filter by IP address, user, device name, etc.
We're also tracking authentication actions and can trigger alerts when we detect an abnormal number of failed login attempts and other suspicious authentication behavior that might indicate credential stuffing or brute force attacks.
Snowflake user's login was blocked by network policy, which could indicate the account was compromised.
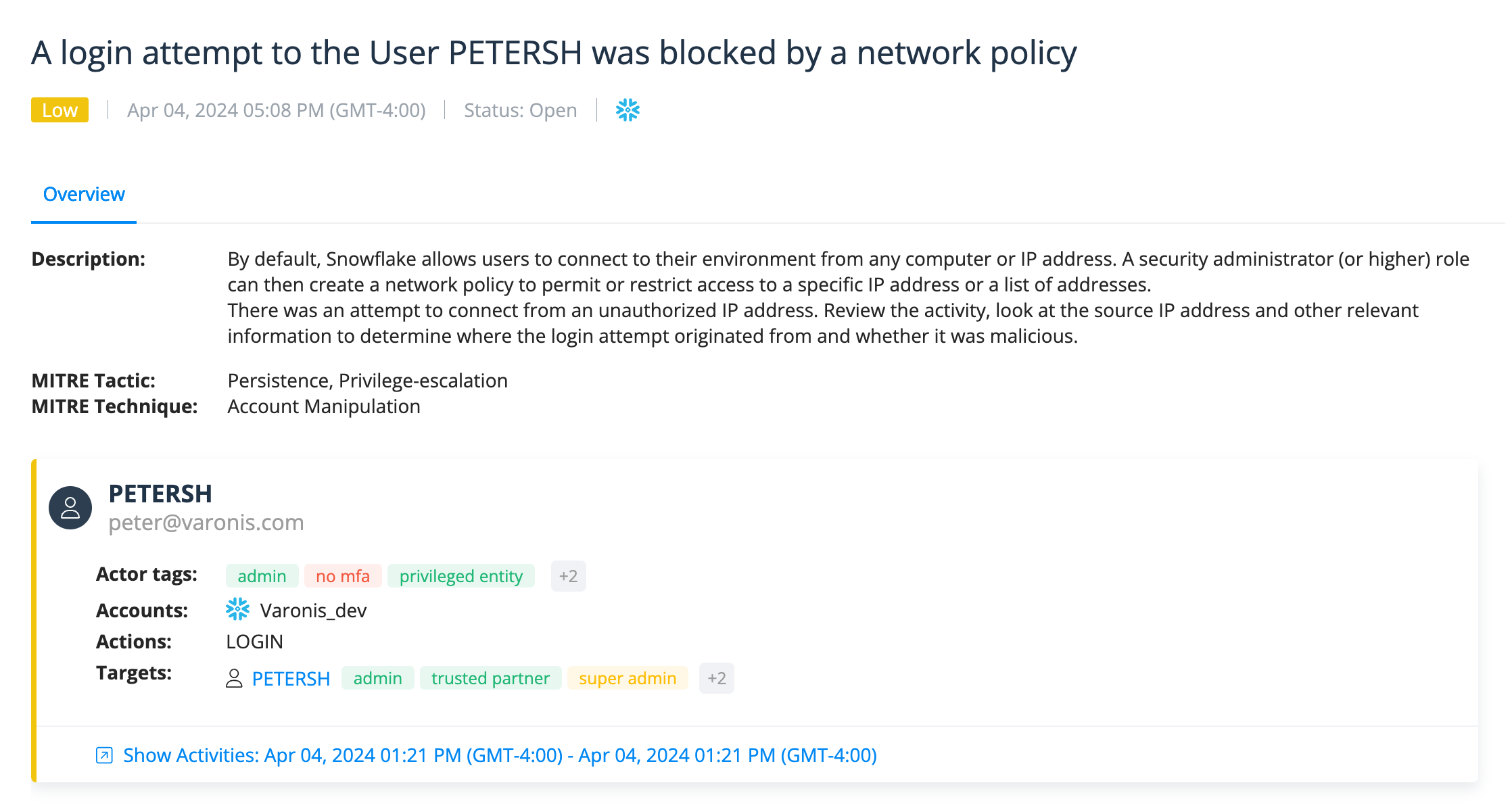
Snowflake user's login was blocked by network policy, which could indicate the account was compromised.
Step 4: Check your network access policies
You can create a policy in Varonis to alert you whenever a Snowflake resource doesn't have a network access policy set to limit who can connect to your Snowflake instance. Use this feature to notify you of any resources missing a network policy and configure the source IPs that should be allowed to connect.
Step 4: Review Snowflake misconfigurations surfaced in Varonis' posture screen such as resources without network policy. Take corrective action based on the recommendations provided.
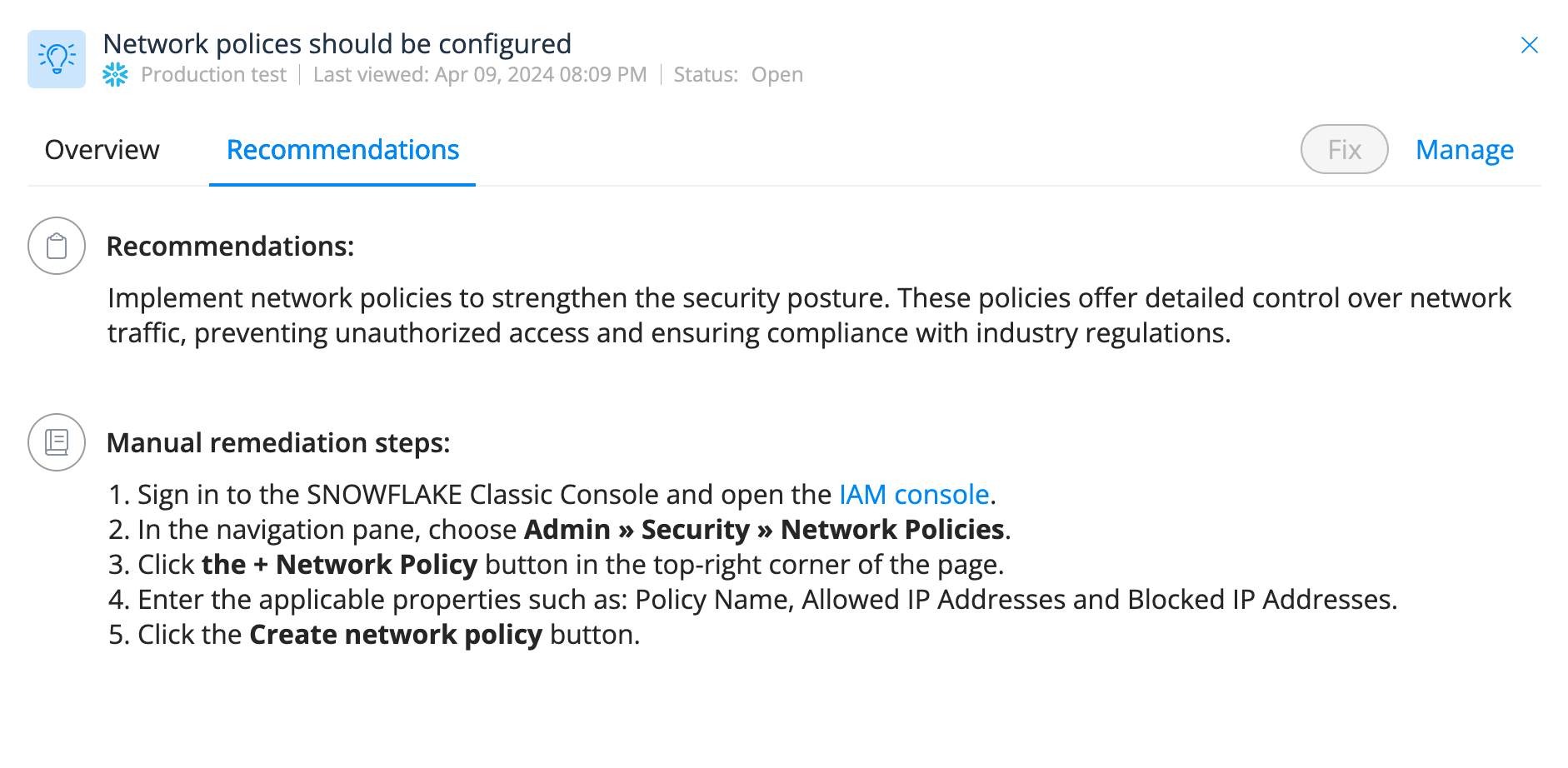
Step 4: Review Snowflake misconfigurations surfaced in Varonis' posture screen such as resources without network policy. Take corrective action based on the recommendations provided.
Step 5: Enable user behavior analysis on your Snowflake logs
You can use Varonis to perform advanced, behavior-based threat detection on Snowflake or pipe your Snowflake logs to a SIEM/XDR; either way, be sure to include Snowflake telemetry in your threat modeling.
One benefit of using Varonis for UBA is that a user's Snowflake behavior is analyzed in context with data sensitivity and correlated to data-related behavior across other platforms like AWS, Azure, Okta, Google, etc. Another benefit is that our threat models are created by Varonis Threat Labs, so you don't have to write manual detections (though you're welcome to!).
In addition to the steps recommended above, we also encourage these best practices to help prevent cloud data breaches:
- Avoid uploading sensitive data to unprotected demo/sandbox accounts and ensure all data in cloud services is protected.
- Enforce MFA for all employees who access sensitive data, both internal and customer data.
- Adopt secure practices for non-human system interactions by limiting static credentials. Instead, use key pair authentication or OAuth as modern alternatives.
Need additional help?
If you are a Snowflake customer who is not currently using Varonis and need assistance securing and monitoring your data, please reach out to our team.
Malicious IP addresses
- 104.223.91.28
- 198.54.135.99
- 184.147.100.29
- 146.70.117.210
- 198.54.130.153
- 169.150.203.22
- 185.156.46.163
- 146.70.171.99
- 206.217.206.108
- 45.86.221.146
- 193.32.126.233
- 87.249.134.11
- 66.115.189.247
- 104.129.24.124
- 146.70.171.112
- 198.54.135.67
- 146.70.124.216
- 45.134.142.200
- 206.217.205.49
- 146.70.117.56
- 169.150.201.25
- 66.63.167.147
- 194.230.144.126
- 146.70.165.227
- 154.47.30.137
- 154.47.30.150
- 96.44.191.140
- 146.70.166.176
- 198.44.136.56
- 176.123.6.193
- 192.252.212.60
- 173.44.63.112
- 37.19.210.34
- 37.19.210.21
- 185.213.155.241
- 198.44.136.82
- 93.115.0.49
- 204.152.216.105
- 198.44.129.82
- 185.248.85.59
- 198.54.131.152
- 102.165.16.161
- 185.156.46.144
- 45.134.140.144
- 198.54.135.35
- 176.123.3.132
- 185.248.85.14
- 169.150.223.208
- 162.33.177.32
- 194.230.145.67
- 5.47.87.202
- 194.230.160.5
- 194.230.147.127
- 176.220.186.152
- 194.230.160.237
- 194.230.158.178
- 194.230.145.76
- 45.155.91.99
- 194.230.158.107
- 194.230.148.99
- 194.230.144.50
- 185.204.1.178
- 79.127.217.44
- 104.129.24.115
- 146.70.119.24
- 138.199.34.144
- 185.248.85.14
What should I do now?
Below are three ways you can continue your journey to reduce data risk at your company:
Schedule a demo with us to see Varonis in action. We'll personalize the session to your org's data security needs and answer any questions.
See a sample of our Data Risk Assessment and learn the risks that could be lingering in your environment. Varonis' DRA is completely free and offers a clear path to automated remediation.
Follow us on LinkedIn, YouTube, and X (Twitter) for bite-sized insights on all things data security, including DSPM, threat detection, AI security, and more.








