Endpoint security is the discipline of locking down any element of an organization that is capable of obtaining internal access to resources such as databases or servers. It is a broad topic that forces cybersecurity professionals to look at every possible access route that a hacker might take in launching an attack.
When hackers look to execute an attack on an enterprise, they first choose what kind of mechanism they will look to exploit. This could be a website, a piece of software, or a networked device. Then they go about hunting for ways put their plan into motion, all while trying to hide their activities from defense systems.
Get the Free Pentesting Active
Directory Environments E-Book
In this article, we’ll explore what endpoint security really means in practice and how companies should implement it into their IT security strategies to help keep their workplace’s cybersecurity practices in check.
See our upcoming security webinars for tips, insights and the opportunity to earn CPE credits.
Why is Endpoint Security Important for Businesses?
In the early days of the internet, when companies were just starting to adopt new computing technologies into their environments, local networks had very clear and rigid perimeters. To access central repositories and servers, you had to be physically situated in the same office and go through a common portal.
In the modern workplace, with the shift to cloud hosting and software-as-a-service, the situation is entirely different. You have employees, partners, and vendors all connecting to your enterprise network from their own devices and often from remote locations. This has made it easier to conduct business globally, but it’s also introduced a range of new cybersecurity threats that organizations must face on a daily basis. Don’t forget that a high portion of cyberattacks come about due to insider threats.
The practice of endpoint security forces enterprise IT teams to look at all possible entrances that outsiders may have to their internal network. What is considered an endpoint? Every new device that employees use, including smartphones and tablets, represents an emerging risk and another vulnerability to consider.
How Endpoint Security Works
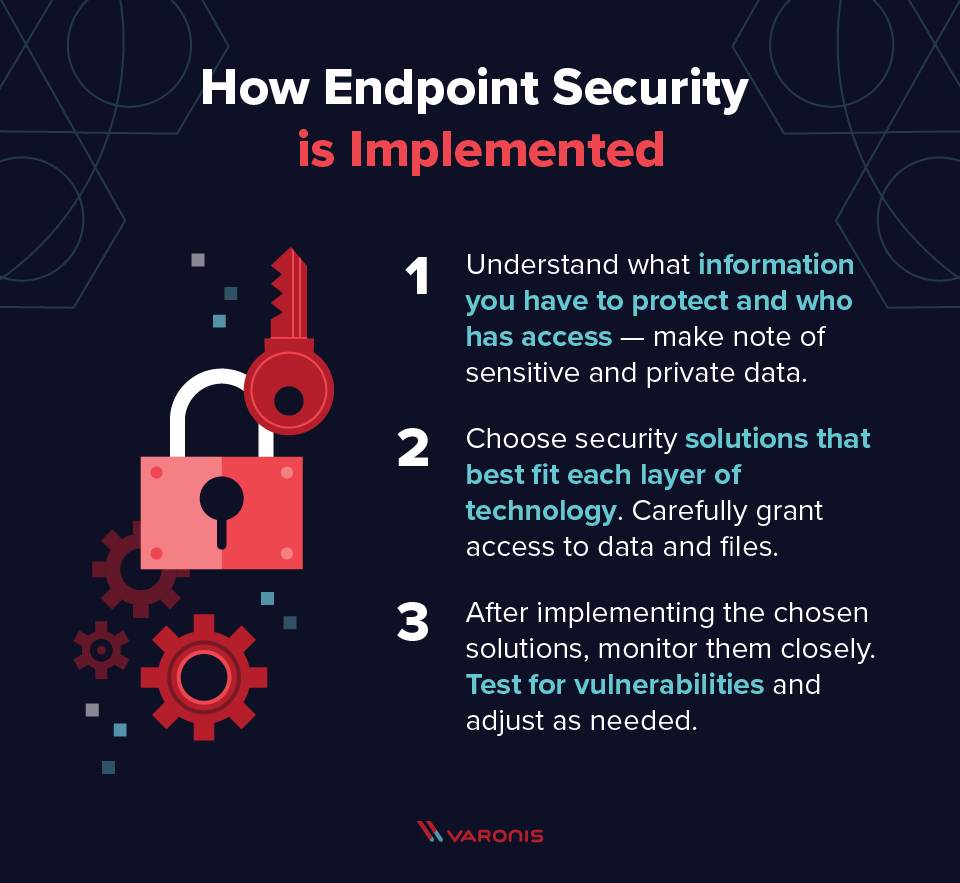
In order to select the best endpoint security protection for business, it’s important to understand how endpoint security interacts with the other elements of security and how to differentiate it as well. Let’s first run through the fundamental process of implementing endpoint security, which every organization needs to consider, regardless of their industry.
- The first step a company must take is information gathering. You won’t be able to defend your network from attack unless you have a complete understanding of all the access points that connect to it. This activity should also cover Identity and Access Management (IAM) so you know who needs access to what resources.
- After surveying and cataloging the various endpoints on your network, you’ll need to choose a security solution for every layer of technology. This includes hardware protection, software protection, cloud protection, and network protection. Keep in mind that certain vendors may offer a suite of services to cover your full range of needs.
- At this point, you are ready to implement the selected solutions and switch to monitoring mode. You’ll need to closely test and measure how each solution performs and determine whether any major network vulnerabilities still exist. If they do, you start the entire process over again.
Now we’ll dig into the precise elements of an endpoint security policy by examining how different tools interact. We’ll cover networks, antivirus programs, firewalls, and cloud environments.
Endpoint Security and The Network
It’s easiest to think of a computer network like a map of a city’s roads. Each path allows people – or, in this case, data packets – to travel from one point to another. Some roads offer faster speeds than others and also allow for travel outside of the primary zone, also known as the local network.
When it comes to endpoint security, it’s important to define what the perimeter of your local network is. All of your key business servers, databases, and applications should reside within the local network. They may be distributed between various pieces of cloud infrastructure, but thanks to the magic of IP addressing, they can all be controlled inside of a single network.
The practice of endpoint security requires you to examine the perimeter of your local network and trace every incoming connection that attempts to penetrate that wall. Each request, regardless of what type of device or user generates it, is considered a threat to your endpoint security. Tools like Varonis Edge allow you to automate the protection of your network.
Difference Between Antivirus Software and Endpoint Security
When comparing antivirus software to a full endpoint security solution, the differences all come down to scope. An antivirus tool is designed to run on a single computer or device and scan its contents to look for known malware or other dangerous files such as the ones linked to recent cryptojacking attacks. Most antivirus programs get updated frequently and will automatically quarantine suspicious data.
On the other hand, an endpoint security solution looks at the entire organization’s network, not just a single device. It runs scans at the edge of the network’s perimeter to identify, flag, and block potential malware. Every new device that comes into the network is automatically included in the endpoint protection.
Endpoint Security and Firewalls
In the early days of the internet, firewalls were typically hardware devices that were directly connected to your main network portal. Most of today’s firewall solutions are software-based but still accomplish the same goal: monitoring all incoming web traffic and filtering out certain IP addresses based on user-set policies.
Some organizations make the mistake of assuming that a strong firewall can serve as a comprehensive endpoint security solution. That is not the case, especially for companies that have a high percentage of people working remotely. A full endpoint security strategy must account for these external connections, which a firewall cannot always monitor or control.
Endpoint Security in the Cloud
The cloud computing movement has introduced a wide range of benefits for software companies of all sizes. Now instead of wasting time, money, and resources managing and maintaining local servers or data centers, you can simply rent computing power from a cloud hosting provider.
But one of the downsides to a cloud-based infrastructure is new complexity when it comes to security. Every access level in your cloud architecture becomes a new endpoint that must be protected. When managing your internal risk, keep in mind that your hosting provider’s security reputation will play a key role in your endpoint reliability.
Managing Endpoint Security
As discussed before, antivirus tools that run on a single device usually require little maintenance and will run in the background without any required user interaction. The same is not true for full-scale endpoint security solutions. These often need a dedicated IT team to monitor and maintain.
It’s important for organizations to think of endpoint security as an ongoing process. Blocking a certain piece of malware or suspicious IP address is not enough to ensure future security. Hackers and cybercriminals are constantly developing new forms of attack and in order to stay safe, endpoint security managers must be ready to tune and adjust their suite of tools.
Selecting the Best Endpoint Security for Your Business

Most organizations hopefully have a baseline of IT security measures in place already. So when looking at the topic of endpoint security, they have to decide whether to abandon their current toolset and invest in a brand new suite or else look to add on individual components to fully meet their needs.
Obviously, cost is a major factor when selecting an endpoint security solution. Vendor pricing will typically vary depending on how many users your company has and how large of a network you are operating. Keep in mind that, depending on what industry or sector your business operates in, that might dictate certain security protocols or regulations that you must follow.
Key Components of Endpoint Security
When doing comparison shopping for an endpoint solution, you need to look closely at exactly what you will be receiving for your investment. Some vendors claim to offer a complete suite but may actually be lacking certain components that other options include. Here are the main elements to look for:
- Device Protection – How does mobile endpoint security work? Your solution should include antivirus and malware protection for both computers and mobile devices like phones and tablets, protecting against attacks like ransomware.
- Network Controls – The endpoint security system should function like a comprehensive firewall that filters all incoming traffic and identifies potential risks.
- Application Controls – This involves integration with application servers to monitor and limit the kind of endpoint access they have.
- Data Controls – This includes tools that help to prevent data leaks and improve data security with encryption of sensitive information.
- Browser Protections – Endpoint security systems often include a web filter option so that you can choose what types of sites your users are allowed to access while connected to the network.
Types of Endpoint Security
One of the big decisions that a company must make is whether to invest in an on-premises or cloud-based endpoint security solution. Cloud options are more flexible and easier to adapt to your existing architecture. However, certain government or industry regulations may dictate that your security tools must reside on-premises at all times.
At the enterprise level, you will want to consider a holistic package like the Endpoint Detection and Response suite from Varonis. This goes beyond simple issue monitoring and alerting. A full response solution includes advanced analysis and forensics on all security incidents.
When considering different endpoint security solutions, make sure to research the different types of products that are available.
- Endpoint Encryption – This functions similar to a virtual private network client (VPN) and is responsible for encrypting all web traffic that leaves your systems. The risk of data leaks and breaches can be minimized if you keep all outgoing transmissions encrypted.
- Forensic Analysis – Tools that specialize in forensics allow you to dig deeper into known issues and diagnose where problems are starting within your network.
- IoT Protection – If your organization relies on smart, internet-connected devices like sensors or instruments, known collectively as the Internet of Things (IoT), you will want to add an extra layer of cybersecurity around them.
- Email Gateways – A large number of cyber-incidents begin through phishing scams and other email-based attacks. By adding email gateway security to your endpoint strategy, you can block suspicious messages from ever reaching your users.
- Quarantine Protection – Some endpoint security solutions will help you create a quarantine area where you can put systems or databases when you believe they are carrying a high level of risk.
Endpoint Security FAQs
In most cases, endpoint security vendors will lock you into a yearly contract, especially if you have selected a cloud-based package. To help make sure you are picking the best option, let’s look at some frequently asked questions.
Q: What is considered an endpoint?
A: An endpoint is any device, connection, or portal that has access to an enterprise’s internal network.
Q: What are endpoint security tools?
A: Endpoint security tools cover a range of activities that aim to lock down endpoints without interrupting business operations. They look specifically for viruses, malware, and other risks of cyberattack.
Q: Why is endpoint security important?
A: As companies grow, they generally introduce more endpoints to their network. Without a clear endpoint security strategy, this could leave the enterprise at risk for attacks from outsiders.
Q: Which is the best endpoint security?
A: The best endpoint security is dependent on your specific needs. Pay attention to which protections are included and make sure you’re selecting the right suite based on your size and budget.
For modern companies, digital data is often the most valuable asset they have. Investing in a best-in-class endpoint security solution is an important step in protecting your data. Varonis offers a product called Datalert which is capable of detecting threats of a data breach and triggering response processes. This type of tool can be extremely valuable when reviewing your layered security strategy.
What should I do now?
Below are three ways you can continue your journey to reduce data risk at your company:
Schedule a demo with us to see Varonis in action. We'll personalize the session to your org's data security needs and answer any questions.
See a sample of our Data Risk Assessment and learn the risks that could be lingering in your environment. Varonis' DRA is completely free and offers a clear path to automated remediation.
Follow us on LinkedIn, YouTube, and X (Twitter) for bite-sized insights on all things data security, including DSPM, threat detection, AI security, and more.









