Companies are under pressure to keep data safe, plus act both swiftly and transparently in the event of a data breach. Slow responses to breaches result in fines from (sometimes multiple) federal entities, loss of customer trust, time lost to the breach instead of business operations, and so much more. These breaches seem to become more public and far reaching as time goes on. One positive thing we can pull from this is the opportunity to learn and prepare our own companies for potential breaches.
We took a deep dive into response times from past data breaches and identified trends to see what went wrong, what went right, and what we can do to prepare. You can take some time to get familiar with data breach response plans before we get started or jump to the section you’d like to dive into first.
Get the Free Essential Guide to US Data Protection Compliance and Regulations
Table of Contents
What is a Data Breach Response Plan?
A data breach response plan is a strategy put in place to combat breaches after they occur to diminish their impact. A well thought out plan ensures every person in a company knows their role during a breach to discover, respond and contain it in a timely manner. These plans provide peace of mind during a crisis since the steps are already tested and laid out, as opposed to formulating a plan in the midst of a breach.
The cost of a breach goes beyond the amount of data lost or disclosed depending on the time it takes to find it. On average, companies take about 197 days to identify and 69 days to contain a breach according to IBM. This lengthy amount of time costs businesses millions of dollars. Companies that contain a breach in less than 30 days save more than $1 million in comparison to those who take longer. Companies also face major fines if they take too long to disclose the breach and put themselves at risk of lawsuits from consumers and independent agencies. The cost alone of notifying customers about a hack averages about $740,000 in the United States.
In total, a data breach costs about an average of $3.86 million. In addition to monetary loss, customer and employee trust are only two of the many non-financial factors companies have to consider in the instance of a breach.
Three Factors That Impact Data Breach Response Time
Preparation, technology and adherence to privacy laws all make a notable impact for a company’s response time. Take a look at how these different factors play a huge role for businesses.
Preparation
Preparation is a key factor in a company’s response timeliness. According to a Centrify study, stock values for companies with a high security posture recovered faster after a data breach. High “security posture” in this study is identified by companies who had the following:
- Fully dedicated CISO
- Adequate budget for staffing and investment in enabling security technologies
- Strategic investment in appropriate security enabling technologies, especially enterprise-wide encryption
- Training and awareness programs designed to reduce employee negligence
- Regular audits and assessments of security vulnerabilities
- A comprehensive program with policies and assessment to manage third-party risk
- Participation in threat-sharing programs
The study further found that highly secure companies showed a quick reaction to the data breach and saw recovered stock values after only seven days. Companies with low security, on the other hand, saw a generally long-lasting decline in stock value after the breach that lasted more than 90 days. This indicates that overall planning makes the difference between a costly and minimal breach.
Having a dedicated team, for example, is a top security tactic to implement as soon as possible. The average cost per lost or stolen record is $148. When a business has a team in place to manage breaches, the average cost savings is $14 per record and these savings make these teams extremely vital. Each member of the team should have a dedicated role in the process. It’s also important to put this team through practice drills to prepare them in the case of an emergency, and continually test the plan to identify any changes needed to improve efficiency or adjust any changes in the company.
Technology
Technology is another element that plays a big factor in a company’s response time, security automation in particular.
IBM also found that companies that fully deploy security automation have an average breach cost of $2.88 million whereas companies without automation have an estimated cost of $4.43 million. Automating different security tasks saves time and money in several ways. It quickly completes time-consuming tasks that keep security and IT personnel from other higher-level assignments. Automation also eliminates the chance of human error and increases your chances of detecting a security threat. This is why cybersecurity solutions that give you a panoramic view of your data are vital to your data breach response strategy.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices, however, are a negative influence for response times. IBM found that the extensive use of IoT devices increased the cost of the breach by $5 per compromised record. These devices are susceptible to hacking since they are constantly connected to the internet and usually have subpar security protection. Some employees also disregard simple things like software updates to increase the security of these gadgets. This means that you should think twice about using things like office assistants in the workplace. If you choose to keep these devices, make sure you keep everything up to date and routinely change passwords.
Privacy Laws
National and statewide privacy laws are relatively new regulations that affect many aspects of a business. These regulations often have specific rules in for notification times.
The GDPR, for instance, requires companies to report data security incidents within 72 hours. Failure to abide by this can result in fines as high as €20 million or 4% of the company’s worldwide annual revenue of the previous financial year.
The NYDFS cybersecurity regulations also require a 72-hour notification in the event of a cybersecurity event, and California’s pending CCPA is also expected to have a similar requirement.
Data Breach Response Times Compared
We can learn a lot when we compare breaches against different factors. For example, looking at average times to identify and contain breaches show us the fastest-responding industries and strategies we can replicate from them. Peruse the comparisons below and see how at-risk your company is compared to others.
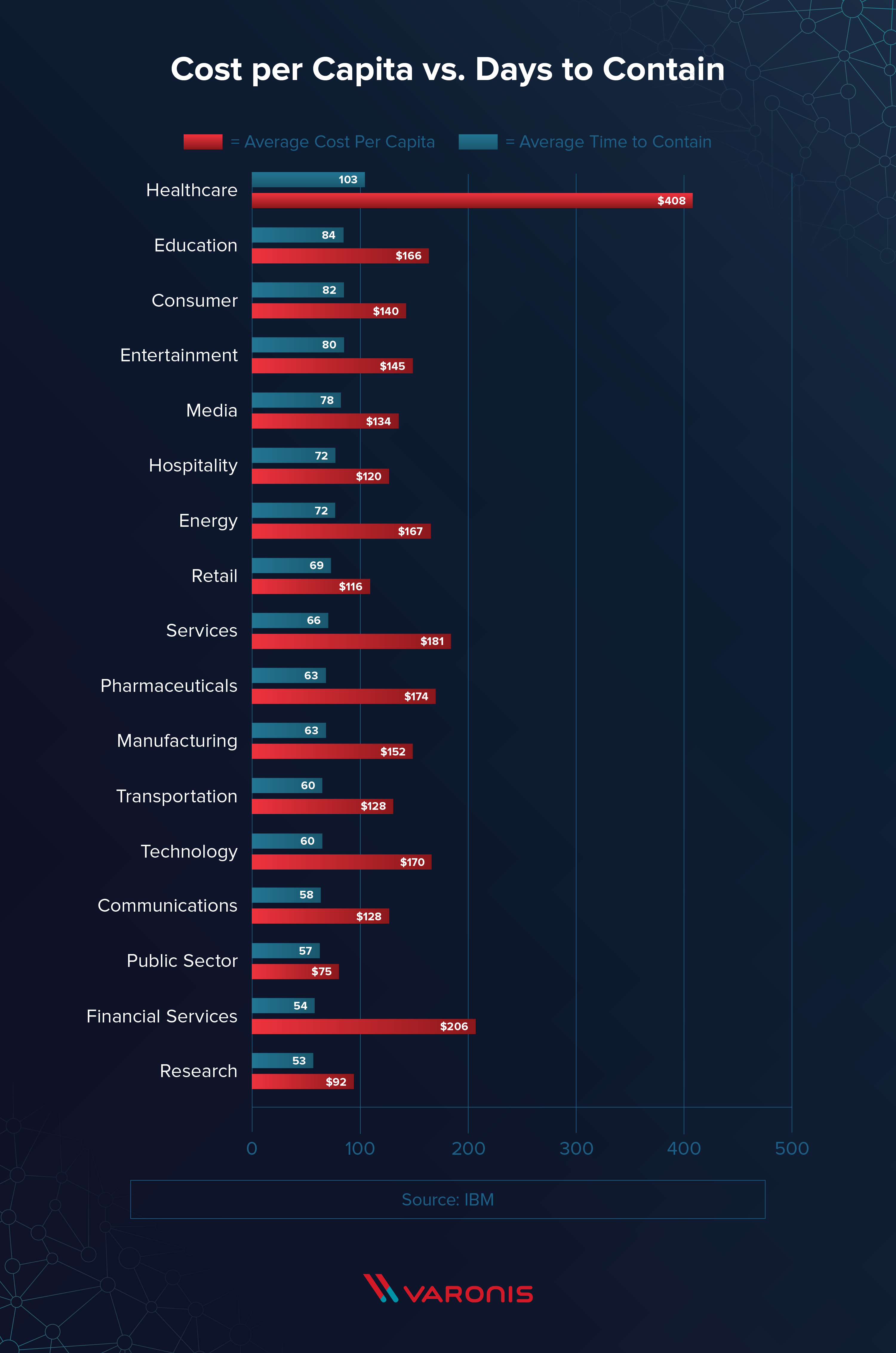
Average Time to Detect and Contain by Industry
The entertainment industry takes the longest to respond to data breaches while the energy industry takes the least amount of time.
It’s important to note that, although the energy industry is the fastest, businesses in this sector still take longer than 30 days on average to find a breach. This means that there is still much to be done to improve response identification across the board.
The average time to contain a breach, on the other hand, is significantly less on average than the time it takes to identify the breach. Healthcare tops the list, taking 103 days to contain a breach while the research industry takes only 53 days.
Identification and Containment Compared to Cost by Industry
Healthcare stands out here as one of the most costly industries to have a breach. This is likely because they have one of the longest average response times to detect a breach.
On the other end of the spectrum, financial services take the least amount of time but still have a high cost per capita. This is most likely because this industry is highly regulated (like healthcare) with regulations like PCI DSS, SOX and more that result in hefty fines.
Data Breach Response Time Trends
There’s a lot to learn from previous data breaches if we dig past the numbers. The average times and costs teach us about the mistakes to avoid and the tactics to implement to strengthen our company’s security. Here are some common trends among data breaches that can inform your team’s data breach response plan.
Companies with dedicated, trained teams and tested response plans respond faster. A dedicated team is crucial to a solid incident response plan. It clearly defines who is responsible for what and ensures that all bases are covered, ranging from public relations to cybersecurity. Defined roles also make it easier for this core group to test different plans and scenarios to prepare them for future attacks.
IoT devices increase the average cost of a data breach. IoT devices open companies up to a new world of risks and vulnerabilities since these devices are becoming more prevalent in office settings. The multiple internet touchpoints created with these devices increase the number of vulnerabilities physically and digitally present around the workplace.
Hackers can easily attack things like office assistants if proper security protocols aren’t followed, like changing the default passwords for a device and connecting it to a secure network. Once hackers are in, they can do things like abuse microphones and cameras to record sensitive conversations.
Security automation decreases the average response time. Automating mundane and time-consuming security tasks efficiently allocates your IT and security team’s time to higher-level security duties that allow them to take a deeper look into potential threats. Security automation also assists with detecting vulnerabilities that security teams may potentially miss due to human error.
It’s faster to contain a breach caused by human error versus a breach caused by malicious attacks. Malicious attacks and hackers are inherently stealthy because they don’t want to be caught. Breaches related to employee error are easier to detect since employees are often unaware of the breach and are not trying to hide it. Although it’s faster to contain this type of breach, it doesn’t make it any less important. Erroneously sending files, opening malicious emails and unknowingly downloading malware can spell disaster for any unsuspecting company, especially if that particular employee had wide-reaching access to company assets.
The faster the data breach is identified and contained, the lower the costs. Overall, data breach costs are significantly less if caught early. Hackers today are stealthy and fast, so it doesn’t take much to compromise sensitive information. The more barriers and precautions you can put in place between data and the hacker, the longer you have to find threats. Preparation and tested response plans also speed up response times to stop hackers before any more damage occurs.
Major Data Breaches and Their Response Times
High-profile breaches are great places to start when formulating a response plan, especially if a company similar to yours is breached. A common trend between many recent breaches is the lengthy amount of time it took them to detect, contain and notify customers about the breach.
Take a look at how these major companies reacted to their breaches and what things they could have done to speed up their response time.
Uber’s major mistake with their hack was the gap between the time of detection and time of notification. Hackers stole credentials from Uber’s GitHub account to access Uber user data stored on an Amazon server. Hackers found their way to sensitive information that affected millions of Uber users including driver’s licenses, email addresses and phone numbers.
Instead of notifying customers and authorities right away, Uber instead paid hackers $100,000 to delete the stolen data and keep quiet on the incident resulting in massive fines, heavy security requirements, monitoring from the FTC, and lots of lost trust among customers and employees.
Uber should have consulted with key personnel within the company, including members from their public relations, IT, legal and security teams, to formulate an ethical way to manage the breach and notify the public. If this plan was made prior to this breach, the company would have had a way to both quickly contain the breach and deliver news of the breach in a timely manner.
Uber’s legal and compliance personnel in particular should have had data breach notification laws top of mind at this time. Although this breach occurred prior to the GDPR’s implementation and rise of other similar privacy laws, 48 states in the United States at this time had security breach notification laws that required companies to disclose news of a hack.
Finally, Uber should have done its due diligence to assess the security risk of all services its employees use. The incident may have been avoided or at least delayed if Uber were routinely checking for suspicious activity and vulnerabilities including employee login credentials and the amount of information they allowed to be stored on third party servers.
The recently uncovered Marriott breach is one of the largest breaches of consumer data to date. The hack affected millions of guests and compromised sensitive information like mailing addresses, passport numbers, Starwood Preferred Guest account information, reservation dates and more.
At the beginning of their acquisition of Starwood Hotels and Resorts, Marriott should have involved their CIO and IT teams to analyze the company from a cybersecurity perspective. Early detection could have either prevented Marriott’s acquisition of Starwood or prompted Starwood to fully contain the breach prior to the acquisition.
Starwood reported a smaller breach involving their POS systems in 2015 and although Marriott claims it was unrelated, cybersecurity experts say that a deeper investigation could have uncovered a relationship between this breach and the breach of their reservation system. This is why it’s important to have an in-depth look at potential companies during mergers and acquisitions.
Marriott should have also implemented a more comprehensive and in-depth cybersecurity solution to supplement their cybersecurity efforts. An internal security tool notified them of a threat September 8, 2018 — four years after the breach started. A stronger tool coupled with more diligent and routine security audits could have helped them find the breach sooner.
Prioritization is another thing to keep in mind when it comes to managing large quantities of data. Some data, like customer information stored in a reservation system, is more sensitive and more important to keep secure over others. Increased prioritization can include more routine audits, more dedicated time to managing the data and a larger overall portion of the cybersecurity budget put towards securing those specific data assets.
The Target data breach in 2013 is a lesson in detection time. Target detected the breach 16 days after the breach started. Although they responded quickly, it was not quick enough to mitigate the damage already done. In that time, attackers compromised payment and contact information of 110 million people with only 11 gigabytes of data.
Target spent $202 million overall on this breach while spending close to $20 million alone on claims. The company also saw a drop in shares and profit in the following quarters and also laid off hundreds of employees following the breach.
The business could have expedited and maybe avoided the entire breach if they had more diligent and routine checks for suspicious activity. Finding the threat and eliminating any vulnerabilities early on could have saved Target a lot of time and money. Automated security tasks could have further helped their security team’s efficiency since they could have instantly found the threat or, even better, found and fixed the vulnerability itself before the hackers could exploit it.
Something else they could have done was limit file access for third-party vendors and others in the company. Since the third-party vendors had lots of access to Target’s information, the hackers only needed stolen credentials from one vendor to access Target’s sensitive information. Limiting file access to those who only absolutely need it helps reduce the risk of hackers accessing sensitive files.
One other major precaution they could have taken was to encrypt and separate cardholder data. The more barriers you can put between attackers and your sensitive information, the longer the time period you have to detect suspicious activity or the breach in progress.
How to Decrease Your Data Breach Response Time
Now we know that the quicker the response, the lower the impact. Here are a few ways you can decrease your data breach response time and save your company time and money.
It’s important to take a proactive approach to data breaches to speed up response times and mitigate as much potential damage as possible. Implementing solutions like Varonis Edge allows you to track suspicious activity around the perimeter to help you quickly identify and shut down possible threats. If you want to get a better idea of where to start, take a data risk assessment to get a clear idea of where you stand and what steps your company can take to prepare for future risks.
Sources
IBM | Centrify | Pew | Experian 1, 2 | GDPR | NBC 1, 2, 3 | ZDNet 1, 2, 3, 4 | IB Times | USA Today | Bloomberg 1, 2, 3 | The Verge | CNN 1, 2 | Tech Crunch | New York Times | Vox | Wall Street Journal | Forbes
What should I do now?
Below are three ways you can continue your journey to reduce data risk at your company:
Schedule a demo with us to see Varonis in action. We'll personalize the session to your org's data security needs and answer any questions.
See a sample of our Data Risk Assessment and learn the risks that could be lingering in your environment. Varonis' DRA is completely free and offers a clear path to automated remediation.
Follow us on LinkedIn, YouTube, and X (Twitter) for bite-sized insights on all things data security, including DSPM, threat detection, AI security, and more.